And they seem to be doing their job quite well. Intercom reports that chatbots saved companies an average of $300,000 in 2019. Business leaders are saying chatbots increased sales by around 67%, and that over 25% of all sales started through an interaction with a bot. 25% of customers say they are open to chat with robots instead of human operators as long as their problems are solved.
The main benefits of chatbots from the customers’ point of view are:
- 24/7 availability
- Instant responses, reduced hold times
- Redirecting users to the right team
New tools for building even “smarter” and more scalable software emerge as machine learning technologies and software development solutions using Artificial Intelligence become more and more widespread. Experts foresee a bright future for such robots. Gartner predicts that by 2022, 70% of customer interactions will involve machine learning apps, chatbots, and mobile messaging.
“Chatbots are still a young industry. Although AI is a widespread term in today’s world, in fact, it is quite a complex area, still in development, and not everyone knows how to make it work for their business. However, as the industry matures, chatbots are likely to become much more sophisticated and able to provide better, more complex solutions compared to what we have today.”
— Gary Vela, CEO at Web Daytona
The Early Life of Chatbots
In 1966, Joseph Weizenbaum, a Professor at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, developed ELIZA, the first chatbot. ELIZA imitated a therapist asking open-ended questions and reacting with follow-ups. It mimicked human conversation, pairing the words entered by the user to a list of possible responses.
In the following decades, automated telephone systems used simple algorithms to conduct basic interactions with callers. But it was not until late in the Internet-era when chatbots as we know them appeared. In the 2010s, popular messengers started to open up their APIs to e-service developers, leading to the spread of this technology. Nowadays, it’s hard to find a big company that’s not equipped with some kind of bot to answer customer questions.
Rule-based or decision-tree bots, similar to ELIZA, are still popular. They are no longer restricted to text interactions and can use either very simple or complicated rules. Such chatbots are easy to build and, as a result, don’t demand much money or time to be implemented. At the same time, they are highly adaptable and can hand conversations to a human if their database is insufficient to answer questions.

These bots have an obvious downside: you can’t provide rules for all possible scenarios. New rules don’t emerge through interactions, so bots need to be updated regularly. A human intervention is likely to be required at some point. Additionally, bots can be useful only within the domains they are designed for. Thus, they cannot be scaled.
The New Age - AI Chatbots
In recent years, following advancements in Artificial Intelligence, a new generation of bots emerged. They are much more sophisticated and need more time, money, and data to build. However, a machine learning chatbot is more efficient and scalable in the long run than a rule-based one. Such programs:
- learn and improve from new data;
- have a broader range of decision-making skills;
- detect behavior patterns;
- can understand many languages.
Those bots use natural language processing (NLP) technologies to determine user intent and help them. With an AI chatbot online, solving customer’s problems requires little human assistance.
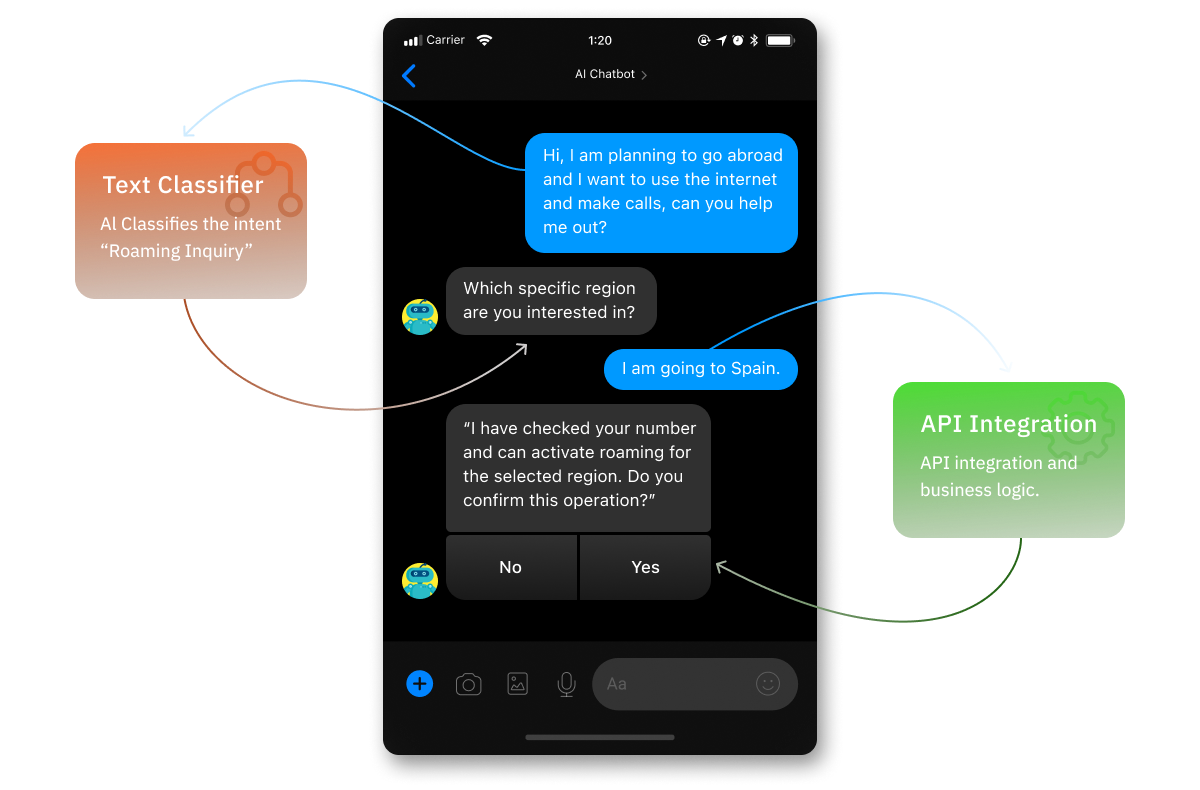
Users can ask the bot a question as if they were talking to other humans. An AI text classifier allows it to decipher the meaning of the question. Using the dialogue tree, the bot asks a sequence of other questions. The answers help to point out the issue to be solved and the best way to do it. The bot can provide users with information, or a link to self-service instructions. But with access to the API of the back-end systems, it can perform the tasks they require.
The most advanced AI chatbots can even learn to distinguish customers’ emotions and interact with humans according to their mood. An example of such technology is Emotibot, developed in China. A self learning chatbot can provide personalized customer service, increasing customer engagement. As AI bots are able to handle queries end-to-end, little to no human participation will be needed to establish 24/7 customer service.
Chatbot Trends 2021
Chatbots might already seem omnipresent, but they have a long way to go. Here are some possible developments in the near future:
- The COVID-19 pandemic will spur use of chatbots. Modern customers are eager to get a seamless experience and instant responses. Intercom’s 2021 Conversation support trends reports that 68% of support leaders who already use chatbots plan to invest more in these technologies in the coming year.
But 2020’s lockdowns and social distancing demands, which are likely to persist in 2021, made online channels of communication even more important. Hence, the demand for automating conversations with customers is growing.
“Custom software development solutions are getting a new boost. Experts report a dramatic increase in the number of bots and conversations with clients in select industries. Besides, large institutions like governments and intergovernmental organizations (for example, the WHO) employ chatbots for different channels.”
— Vlad Medvedovsky at Proxet, custom software development solutions company
- Chatbots are likely to get “smarter.” On the one hand, engineers are pressed by the demands of business. Some customers have reservations about talking to a robot, doubting its ability to provide meaningful outcomes. Bots should help, not annoy or distract. They should be integrated into business processes, providing smooth communication with different departments, like sales, marketing, or support.
On the other hand, more advanced technologies are implemented, allowing conversational bots to act more like humans. In 2020, Google launched Meena, an open-domain chatbot, supporting multi-turn conversation. It is based on a neural network, containing about 2.6 billion parameters and trained on more than 340 GB of text data.
- Voice recognition and multi-modality will get into focus. The popularity of voice assistants is booming. More and more users grasp the advantages of actually telling their smartphone or PC what to do instead of typing some commands. In America, one in three inhabitants uses voice assistants at least once a month.
But the screen can also have its uses. The question is how to mix voice and screen to provide the best user experience.
“It’s an interesting combination of using voice at what it’s really good at—the input modality and then using the UI at what it’s really good at—the output modality and kind of slicing and combining those together.”
— Roger Kibbe, Senior Development Evangelist at Viv (Samsung)
The Best Old and New Platforms for Building Chatbots
There are different ways to build conversational software. For example, to design an AI chatbot Python and the Scikit-learn library can be used.
But there is also a much easier way: chatbot platforms. Actually, even a person without technical knowledge can create a bot using a drag-and-drop approach. Here are some of the best such platforms:
- Chatfuel does not require any programming knowledge. You use different blocks, consisting of cards, which may include messages and other content (text, images, audio, and video). Many multinationals, such as Volkswagen, Adidas, British Airways, use this platform for their Facebook Messenger chatbots;
- Botsify is also a popular chatbot platform for Facebook Messenger that uses drag and drop templates. Machine learning and AI integration are made easy by the pull out template alternatives. You can program the bot to hand the conversation over to a human if required;
- Flow Xo offers an astounding 100+ integrations. You can build chatbots for many platforms at once, unlike with other chatbot platforms. The editor is easy to use, and pre-built templates will help you get started quickly;
- Dialogflow (Google) allows users to develop voice- and text-based AI-powered conversational interfaces. It's integrated with popular messengers like Amazon Alexa, Microsoft Cortana, Actions on Google, etc. Dialogflow is renowned for convenient and functional natural language processing tools;
- Converse.ai has quick-start templates. Users can build it into different third-party platforms, including HubSpot, ClearBit, Stripe, Salesforce, and PayPal. Its analytics engine allows you to track and research interactions between users and your chatbots.
Chatbot platforms are great tools to solve typical tasks. It’s more practical than googling “AI chatbot Python Github” and trying to build something from scratch. But what if your business demands complex, custom solutions?
Proxet can help you build conversational AI software. NLP, voice technology, and chatbots are our specialities. We’ve developed virtual assistants for our clients in the healthcare industry. Our top Artificial Intelligence engineers and machine learning experts do their best to help our clients succeed.Computers help businesses automate more and more tasks—even interactions with humans. “Chatbots” are virtual assistants designed for this purpose. Their main purpose is to provide an effortless customer experience at minimum expense. Chatbots are now used in every industry, from travel to healthcare.



